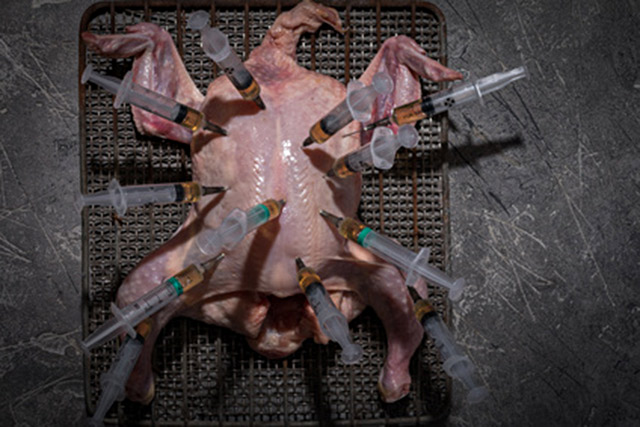
Antibiotics in meat continue to rise despite promises, according to the latest FDA statistics, reported by NPR’s The Salt.
The overuse of antibiotics is now an epidemic in the United States and it is creating antibiotic resistance.
They are prescribed for almost everything.
The issue with taking too many antibiotics is that they kill good bacteria in the gut, which makes it more difficult to fight infections in the future.
The immune system gets used to them and creates antibiotic resistance.
A report published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that in 2010, health care providers prescribed “258.0 million courses of antibiotics in 2010, or 833 prescriptions per 1000 persons.” The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is now reporting that the infectious organisms that antibiotics usually target have adapted to the drugs, because they have been used for so long.
Companies and supermarkets are constantly promising a reduction or banning of antibiotics in their food.
So why are sales of “sub-therapeutic” antibiotics used on swine, cattle and poultry going up?
As written in The Salt:
“Antibiotic sales for use on farm animals increased by 1 percent in 2015, compared to the previous year. The increase was slightly greater — 2 percent — for antibiotics used as human medicine …
But the FDA finds a glimmer of good news in the latest figures, pointing out that the rate of increase has slowed. In the previous year, antibiotic use had increased by 4 percent, and a total of 22 percent from 2009 to 2014.”
Chick-Fil-A announced last year in a statement that they would start serving antibiotic-free chicken. Major corporation Tyson has also reduced antibiotic use by over 84 percent since 2011.
Foster Farms also announced two years ago that they would be eliminating antibiotics in chicken.
“This report further underscores how urgently we need more and stronger government action” to reduce antibiotic use, David Wallinga, from the Natural Resources Defense Council said in a statement.
Note: None of the information in our website is intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any illness or disease. The content on our website is for educational purposes only.
DON’T FORGET to sign up for our weekly newsletter to get our latest articles, updates, free recipes and giveaways.
What you need to know about antibiotic resistance.
Children’s exposure to antibiotics increases food allergy risk.
Antibiotics stop new brain cells from growing.
REFERENCES:
1. “Germs Are Germs, and Why Not Take a Risk? Patients’ Expectations for Prescribing Antibiotics in an Inner-City Emergency Department.” Sage Journals. Medical Decision Making, 20 Oct. 2014. Web. 4 Feb. 2016.
2. “Antibiotic / Antimicrobial Resistance.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 04 Mar. 2014. Web. 4 Feb. 2016.
3. “Chick-fil-A to Serve Antibiotic-Free Chicken.” Chick-Fil-A. Chick-Fil-A, 11 Feb. 2014. Web. 4 Feb. 2016.
4. “Tyson Foods Strives to Eliminate Human Antibiotics From Broiler Chicken Flocks by 2017.” Tyson Foods. Tyson Foods, 28 Apr. 2015. Web. 4 Feb. 2016.
5. “Foster Farms Backs Away from Using Human Antibiotics in Poultry.” Reuters. Thomson Reuters, 01 June 2015. Web. 4 Feb. 2016.
6. “Despite Promises, Antibiotics in Meat Supply Are Skyrocketing.” Mercola.com. Mercola.com, n.d. Web. 04 Feb. 2017.
7. “Despite Pledges To Cut Back, Farms Are Still Using Antibiotics.” The Salt. NPR, n.d. Web. 04 Feb. 2017.